AI Feedback Analysis and Text Analytics
Most teams are drowning in feedback by 2026.
Surveys. Nps comments. Csat verbatims. Call transcripts. Chat logs. App reviews. Social posts.
Everyone agrees the voice of the customer matters, but a quiet question hangs in the air:
• Who is actually reading all this?
• Which issues should we fix first?
• How do we connect what people say to churn, retention and revenue?
This is where feedback analysis using AI and AI text analytics becomes essential.
On this page, we will walk through:
• What does “feedback analysis” really mean in customer experience?
• How AI text analytics works under the hood.
• How to move from generic sentiment to real cx drivers.
• How to design an AI feedback analysis workflow that teams trust
• How ZYKRR and ZYVA turn raw feedback into monetization decisions.
• Prompt ideas you can use in your own LLM or Copilot to explore AI in customer experience.
You can treat this page as the deep dive that sits between the AI in customer experience pillar and the cx monetization pillar.
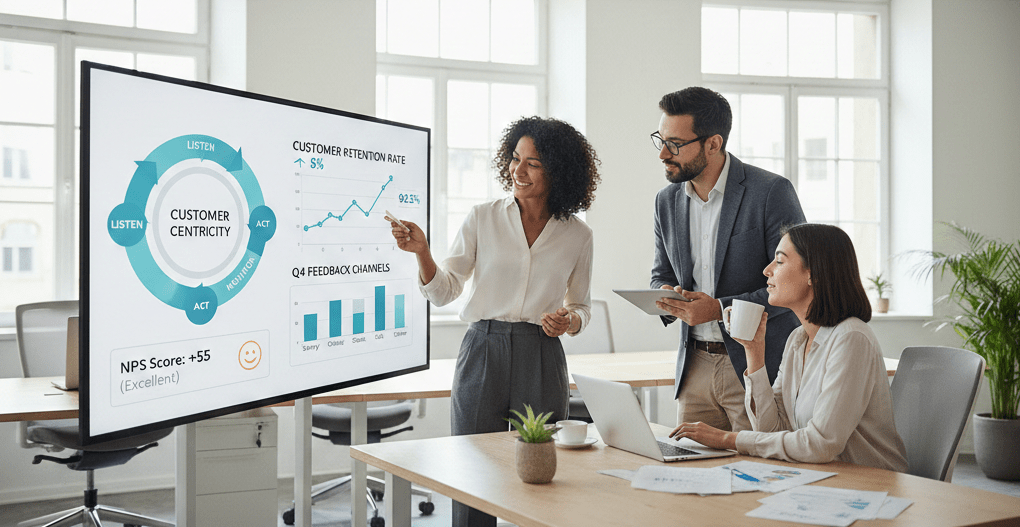
What is feedback analysis in customer experience
When people Google “what is feedback analysis”, they usually find vague definitions.
In practical cx terms, feedback analysis is simply:
A structured way to read what customers tell you, organise it into patterns and link it to actions and outcomes.
That includes:
• Survey comments (“Why did you give this score?”)
• Open-text responses in nps and csat
• Call and chat transcripts
• In-app feedback and reviews
Done well, feedback analysis answers questions like:
• What are customers really complaining about?
• What do promoters love that we should amplify?
• Which issues keep showing up before churn or downgrade?
• Which themes correlate with higher retention or expansion?
Historically, teams tried to do this manually:
• Exports into spreadsheets
• Manual tagging
• Highlight decks with a few choice quotes
It does not scale. That is why feedback analytics and feedback analysis in AI are becoming core to modern cx.
Why manual feedback analysis breaks at scale
A lot of cx teams still rely on human-only feedback reading. The problems are predictable.
Volume and speed
Even a modest B2B or B2C operation can generate:
• Thousands of survey comments per month.
• Tens of thousands of chat lines.
• Hundreds of hours of calls.
Teams cannot read everything carefully and still do their day job. They end up:
• Sampling a small portion of feedback.
• Focusing on loud outliers.
• Missing slow, systemic issues.
Inconsistent tagging and bias
Manual tagging tends to be:
• Inconsistency between people and teams.
• Shaped by what the reader expects to see.
• Hard to keep updated as the product, journeys and language change.
So two people may tag the same comment in two different ways:
Is “too expensive for what it does” about pricing, value, product gaps or competitor comparisons?
Without a common structure, feedback analysis turns into opinion.
Weak link to outcomes
Finally, manual work rarely connects feedback to:
• Churn and retention behaviour
• Customer lifetime value
• Cost to serve and channel usage
You might know that “billing” comes up a lot, but not whether fixing specific billing issues actually improves customer experience roi.
AI does not magically fix all of this, but it gives you a fighting chance.
How AI text analytics works for feedback analysis
The term “feedback ai” or “feedback analytics ai” usually refers to a set of natural language processing techniques that work together.
You do not need the maths. You do need to understand what they do.
1. Classification and intent detection
AI models can read each comment or transcript and decide:
• What topic does it belong to (onboarding, pricing, support, product quality, usability)?
• What is the main intent (wants to cancel, wants to upgrade, is confused, is praising)?
This is where “feedback analysis using AI” starts to pay off. Instead of closing tickets one by one, you can see: “Here are the most common intents by journey and segment.”
2. Sentiment and emotion
Basic sentiment says whether a comment is:
• Positive
• Neutral
• Negative
More advanced models can also estimate emotion:
• Frustration
• Confusion
• Disappointment
• Delight
This matters when you design ai customer service agent behaviours and escalation paths. A short burst of anger in a chat log may deserve a human even if the words are short and simple.
3. Topic and theme extraction
Topic modelling and clustering help group related comments.
For example, thousands of comments might be summarised into themes like:
• Difficulty understanding pricing tiers.
• Delays and a lack of proactive updates in delivery.
• Bugs and crashes on specific devices.
ZYVA goes further and links these themes to outcomes:
• Themes that commonly appear before churn.
• Themes that are common among high-value, long-tenure customers.
• Themes that spike in particular channels or regions.
This is a major step beyond simple “word clouds.”
4. Summarisation and narrative
Generative AI can take hundreds or thousands of comments and answer:
• “In a few short paragraphs, what are customers saying about onboarding this quarter?”
• “How would you explain our support experience to the executive team in simple language?”
This is where phrases like “AI feedback generator” sometimes show up. The best tools do not generate fake feedback. They generate:
• Summaries
• Narratives
• Action lists
based on real signals.
ZYVA is tuned to generate narratives for humans, not vanity text for reports. It focuses on what different roles need to know:
• Frontline teams
• Product managers
• CX leaders
• CFOs and revenue leaders
From sentiment to drivers: what really moves cx
Generic sentiment is not enough. A good AI feedback analysis setup will separate:
“How customers feel”
from
“What is causing those feelings?”
and then link both to outcomes.
Identifying drivers of delight and pain
Drivers are specific, actionable levers such as:
• “speed and clarity of onboarding communication”
• “first response time on critical tickets”
• “stability of core workflows on mobile”
ZYVA can help identify:
• Which drivers show up most often in feedback?
• Which drivers are most associated with high nps, csat and retention?
• Which drivers appear before downgrades and churn?
That is how you move from:
“People are unhappy”
to:
“Customers in this segment with this onboarding issue are three times more likely to churn within ninety days.”
Connecting drivers to the cx monetization story
Once you know the main drivers per segment and journey, you can:
• Prioritise cx initiatives.
• Design experiments to fix specific drivers.
• Use the cx roi calculator and retention roi work to size the impact.
Feedback is no longer a pile of complaints. It becomes:
• A ranked list of levers you can pull
• Linked to cx revenue, cost to serve and customer lifetime value
This is how feedback analysis in AI supports cx monetization.
Designing an AI feedback analysis workflow
To get value out of AI, you need a simple workflow that people can follow and trust.
Step 1: Unify feedback sources
First, bring together:
• Survey comments (nps, csat, relationship and transactional)
• Contact centre transcripts
• Live chat and bot logs
• In-product feedback and simple review snippets
In ZYKRR, the signals suite handles this unification, so ZYVA can see the full picture.
If you start small, pick two or three sources where most customer emotion lives, like:
• Support tickets and their comments
• Transactional surveys after critical journeys
Step 2: Define journeys, segments and questions
Do not throw all feedback into a single bucket. Define:
• Which journeys do you care about (onboarding, support, billing, renewal, cancellation)?
• Which segments do you want to compare (by plan, size, region, lifecycle)?
• Which questions do you need answered?
For example:
• “What are the top drivers of low csat in onboarding for new mid-market customers in North America?”
• “What do our longest-tenure, most profitable customers say about us?”
AI models can then focus on these structured questions, not generic “analyse everything”.
Step 3: Run AI analysis and generate views
Next, turn on the feedback analytics AI pipeline:
• Classification by theme and intent
• Sentiment and emotion analysis
• Driver identification and contribution
• Summaries for each journey and segment
In ZYKRR and ZYVA, this shows up as:
• Dashboards where you can filter by journey, segment, time and theme.
• Driver analysis views that connect themes to churn, retention and expansion.
• Narrative summaries you can use in reviews and decision forums.
Step 4: Review, challenge and refine
AI is not a black box oracle. Build in a review habit:
• Have CX, CS and product leaders sanity-check top themes and drivers.
• Spot where AI is mislabelling or missing nuance.
• Adjust taxonomies, training examples and thresholds over time.
This is where trust is built. Over a few cycles, teams start to see that:
• AI is capturing the bulk of patterns accurately.
• Humans are focusing on review and decision, not raw reading.
Step 5: Connect to actions and outcomes
Finally, plug findings into:
• Journey and product backlog prioritisation
• Closed-loop feedback processes
• Save and expansion plays
Track:
• How do the frequency and sentiment of key themes change over time?
• How do churn and retention patterns shift when you address certain drivers?
• How cost of serving move as you fix or automate specific issues?
This is the full cycle from feedback analysis using AI to cx monetization.
How ZYKRR and ZYVA handle AI feedback analysis
ZYKRR and ZYVA were designed with feedback at the centre.
Multi-channel feedback as first-class signals
The signals suite ingests:
• Survey responses across customer and employee journeys
• Call recordings and transcripts
• Chat and messaging logs
• Behavioural events from products and services
Each item is tagged by:
• Journey
• Segment
• Channel
• Lifecycle stage
So that ZYVA has a rich context when it runs feedback analysis in AI.
ZYVA as the AI feedback intelligence layer
ZYVA focuses on three jobs:
1. Understand: Detect themes, intents, sentiment and emotion across large volumes of feedback.
2. Connect: Link those themes and intents to churn, retention, expansion and cost outcomes.
3. Explain: Produce summaries and narratives tailored to different roles.
Examples of outputs:
• “Top three drivers of detractor nps in onboarding, by segment.”
• “Emerging theme in support for customers likely to churn.”
• “What promoters in this industry say about value and ease of use.”
These are not generic dashboards. They are inputs to monetization and prioritisation decisions.
From AI feedback analysis to closed-loop and monetization
Because ZYKRR is built around the capture → analyze → act → measure → monetize flow, feedback never stops at analysis.
1. Actions: Triggers and playbooks based on ZYVA signals, such as follow-up for detractors or outreach to high-potential promoters.
2. Measure: Tracking csat, nps, journey scores and driver frequencies over time.
3. Monetize: Linking changes in drivers to churn, retention, expansion and cost improvements.
Feedback analysis becomes the starting point of the cx revenue loop, not a one-off research project.
Choosing AI feedback analysis tools and platforms
If you search for “feedback analysis tool,” “feedback analytics,” or “AI customer experience tools”, you will see a long list of options.
When you evaluate them, consider three practical questions.
Does it see the whole customer story?
Tools that only read surveys but ignore calls, chats and product usage will miss important context.
Look for:
• Multi-channel ingestion
• Journey and segment tagging
• Ability to incorporate external data such as churn and revenue
Can non-technical teams use and trust it?
Data science teams are useful, but cx and cs leaders need to:
• Explore themes and drivers themselves
• Understand how the model arrived at a conclusion• Challenge and refine results
Beware of black box tools that say “AI says so” without:
• Showing examples
• Explaining drivers in plain language
• Allowing you to adjust labels and structures
Does it connect to action and roi?
Finally, ask:
• Can this tool trigger workflows, or does it only show charts?
• Can we quantify customer experience roi and cx monetization based on its outputs?
• Does it help us answer “what changed in retention or revenue because of what we fixed”?
Generic AI analytics tools may be good at summarising text. A platform like ZYKRR adds the operational and monetization layers on top of that analysis.
LLM prompt block: Exploring AI feedback analysis in your own environment
You can use your own llm or Copilot to explore AI in customer experience using your data and context. Here are some prompt patterns tuned to your keyword universe.
Design a feedback analysis using an AI workflow for our company
We collect feedback from [list: nps, csat, support tickets, calls]. Design a “feedback analysis using AI” workflow for us. show how to ingest data, run AI text analytics, identify themes and link them to churn and retention. Keep steps simple enough for CX and CS teams.
Explain feedback analysis and AI text analytics to non-technical stakeholders
Explain “what is feedback analysis” and “AI text analytics for customer experience” in simple language. Give two or three concrete examples relevant to [our industry] and show how they can improve cx roi and retention.
Summarise recent customer feedback for an executive cx review
Here are anonymised customer comments from the last month [paste sample]. act as an “ai feedback generator” that only generates summaries and insights, not fake quotes. group themes, estimate sentiment and suggest three actions we should prioritise.
Identify early churn risk themes using feedback analytics AI
Here are comments from customers who churned and those who renewed [provide sample or description]. using “feedback analytics ai” reasoning, identify themes that appear more in churners than in renewers, and suggest how we might detect these earlier.
Draft a one-page guide for agents on how AI helps with feedback analysis
Write a one-page explainer for frontline agents describing how “AI in customer experience” is used to analyse feedback. Reassure them that AI is a support tool, not a replacement, and explain how they can use the insights in conversations.
Used well, LLMs become part of your feedback analysis stack, sitting alongside ZYVA rather than competing with it.
Where to go next
If you want to go deeper on AI in customer experience beyond feedback analysis, the next cluster pages to explore are:
• Emotion AI and behavioural signals in customer experience.
• Designing AI customer service agents that customers actually trust.
• Predictive AI in cx for churn, retention and expansion.
• Strategies for leveraging AI in the customer experience across journeys.
From there, you can loop back into the cx monetization pillar and use everything you learn from AI feedback analysis to fuel:
• Better prioritisation
• Sharper save and growth plays
• Clearer cx roi stories for leadership
If you are happy with this draft, we can move next to the emotion AI and behavioural signals in the customer experience cluster, or to AI customer service agents, using the same structure and tone.